Table of Contents
Understanding the Diet
Key Foods and Nutrients
Cardiovascular Benefits
Cognitive Benefits
Metabolic Benefits
Antioxidant Effects
Practical Considerations
Tips for Adoption
[**The health benefits of the Mediterranean diet**](https://tauhuichiban.com.vn/the-health-benefits-of-the-mediterranean-diet/) are extensive. From heart health to cognitive function, this traditional way of eating offers a wealth of advantages. By learning about its key foods and nutrients, you can reap the rewards of this healthy eating pattern.The Mediterranean Diet: A Journey to Health and Well-being
I. Introduction
Embark on a culinary adventure with the Mediterranean diet, a time-honored tradition that nourishes both body and mind. Rooted in the sun-kissed lands of southern Europe, this vibrant eating pattern has gained global recognition for its remarkable health benefits. Discover the secrets of the Mediterranean diet and unlock a world of culinary delights while safeguarding your well-being on [**Tauhuichiban**](https://tauhuichiban.com.vn/).
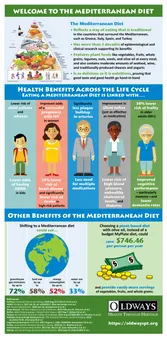
The Health Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet and Its Amazing Power
II. The Health Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Diet
Kick off your culinary journey with the wholesome Mediterranean diet, a nutritional powerhouse renowned for its health-boosting properties. This traditional way of eating, originating from the sun-drenched lands of southern Europe, has gained recognition globally due to its remarkable health benefits. Join us as we delve into the core principles of the Mediterranean diet and uncover the secrets to its nutritional prowess, on The History and Diversity of Mediterranean Cuisine.
At the heart of the Mediterranean diet lies a harmonious blend of nutrient-rich foods, including fresh fruits, vibrant vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. These wholesome ingredients come together to create a symphony of flavors and textures, while providing an abundance of essential vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and healthy fats. Embark on a culinary voyage with The Essential Ingredients and Spices for Mediterranean Cooking and discover the secrets to creating authentic Mediterranean dishes that tantalize your taste buds and nurture your well-being.
Explore the regional diversity of Mediterranean cuisine, from the vibrant flavors of Greece to the hearty dishes of Italy. | |
|---|---|
The Key Nutrients and Health Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet | Uncover the nutritional powerhouse of the Mediterranean diet and its remarkable impact on overall health. |
Key Foods and Nutrients
The Mediterranean diet is an orchestra of nutrient-rich foods that work in harmony to promote well-being. Fresh fruits and vegetables form the vibrant core of the diet, providing an array of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants essential for optimal health. Whole grains, such as brown rice and quinoa, supply a steady stream of energy and fiber, contributing to satiety and digestive health. Lean proteins, primarily from fish, poultry, and legumes, provide the building blocks for strong muscles and tissues.
Healthy fats, predominantly found in olive oil, avocados, and nuts, play a crucial role in the Mediterranean diet. These fats contribute to heart health, reduce inflammation, and support cognitive function. Herbs and spices, such as oregano, basil, and thyme, not only enhance the flavors of Mediterranean dishes but also possess antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Together, these key foods and nutrients synergistically contribute to the exceptional health benefits of the Mediterranean diet.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Apples, oranges, bananas, leafy greens, tomatoes, cucumbers
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, quinoa, oats, whole-wheat bread
- Lean Proteins: Fish (salmon, tuna), chicken, turkey, beans, lentils
- Healthy Fats: Olive oil, avocados, nuts (almonds, walnuts)
- Herbs and Spices: Oregano, basil, thyme, rosemary
Cardiovascular Benefits
The Mediterranean diet has garnered significant attention for its remarkable cardiovascular benefits. The abundance of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides a rich source of antioxidants, which combat oxidative stress and protect against heart disease. Healthy fats, particularly olive oil, contribute to lowering LDL (bad) cholesterol levels while raising HDL (good) cholesterol levels, promoting a healthier lipid profile.
Research indicates that individuals who adhere to the Mediterranean diet have a lower risk of heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular events. This protective effect is attributed to the diet's anti-inflammatory properties, ability to improve blood pressure control, and support endothelial function, the lining of blood vessels. Join us for a deeper exploration of the Health Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet for Cardiovascular Health and discover how this dietary approach can safeguard your heart.
The Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet for Reducing Inflammation | Learn how the Mediterranean diet can combat inflammation, a key factor in chronic diseases. |
|---|---|
The Impact of the Mediterranean Diet on Blood Pressure Control | Discover the Mediterranean diet's positive effects on blood pressure management. |
Cognitive Benefits
Emerging research suggests that the Mediterranean diet may also play a significant role in preserving cognitive health as we age. The abundance of antioxidants, particularly flavonoids found in fruits, vegetables, and olive oil, helps protect against oxidative damage to brain cells. Additionally, the anti-inflammatory properties of the diet may reduce inflammation in the brain, which has been linked to cognitive decline.
Studies have shown that older adults who adhere to a Mediterranean-style diet have a lower risk of cognitive impairment, dementia, and Alzheimer's disease. The diet's ability to support brain health may be attributed to its positive effects on blood flow to the brain, as well as its potential to promote neurogenesis, the growth of new brain cells. Delve deeper into the Link Between the Mediterranean Diet and Cognitive Health and uncover how this dietary approach can safeguard your cognitive well-being.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Berries, apples, leafy greens, broccoli
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, quinoa, oatmeal
- Lean Proteins: Fish (salmon, tuna), chicken, beans
- Healthy Fats: Olive oil, avocados, nuts
- Herbs and Spices: Turmeric, rosemary, sage
Metabolic Benefits
The Mediterranean diet is not only beneficial for heart and cognitive health but also supports metabolic well-being. The emphasis on whole, unprocessed foods helps regulate blood sugar levels, preventing insulin resistance and reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes. Dietary fiber from fruits, vegetables, and whole grains promotes satiety and supports a healthy digestive system.
Healthy fats, particularly monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats found in olive oil and nuts, contribute to metabolic health by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing inflammation. These fats also support hormone production and regulate gene expression, influencing various metabolic processes in the body. Dive into the Metabolic Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet and discover how this nutritional powerhouse can optimize your metabolism.
Explore the Mediterranean diet's potential for aiding weight loss and promoting a healthy weight. | |
|---|---|
Learn how the Mediterranean diet can help prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes. |

The Health Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet: A Comprehensive Guide
III. Nutritional Composition of the Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet is characterized by its emphasis on fresh, unprocessed foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. It is also rich in healthy fats, such as those found in olive oil and nuts. This combination of nutrients provides a number of health benefits, including reduced risk of heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and some types of cancer.
One of the key features of the Mediterranean diet is its high intake of fruits and vegetables. These foods are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which are essential for good health. Fruits and vegetables are also a good source of fiber, which can help to keep you feeling full and satisfied after eating.
Nutrient | Amount |
|---|---|
Calories | 2,000-2,500 |
Fat | 60-80 grams |
Carbohydrates | 225-325 grams |
Protein | 75-100 grams |
Fiber | 25-30 grams |
Another important component of the Mediterranean diet is whole grains. Whole grains are a good source of complex carbohydrates, which provide sustained energy throughout the day. They are also a good source of fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
Lean protein is another important part of the Mediterranean diet. Lean protein sources include fish, poultry, beans, and lentils. These foods are a good source of essential amino acids, which are necessary for building and repairing tissues.
The Mediterranean diet is also rich in healthy fats. Healthy fats are found in olive oil, nuts, and avocados. These fats can help to lower cholesterol levels, reduce inflammation, and improve brain function.
The Mediterranean diet is a healthy and balanced way of eating that can provide a number of health benefits. By following the Mediterranean diet, you can reduce your risk of chronic diseases, improve your overall health, and live a longer, healthier life.

Nutritional Composition of the Mediterranean Diet
IV. Mediterranean Diet and Disease Prevention
The Mediterranean diet is a traditional way of eating that has been linked to a number of health benefits, including a reduced risk of heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and some types of cancer. The diet is based on the foods that people living in the Mediterranean region have eaten for centuries, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
One of the key components of the Mediterranean diet is its emphasis on fruits and vegetables. Fruits and vegetables are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which are all essential for good health. They are also a good source of fiber, which can help to keep you feeling full and satisfied.
Fruit | Vegetable |
|---|---|
Apples | Broccoli |
Bananas | Carrots |
Berries | Celery |
Citrus fruits | Cucumbers |
Grapes | Greens |
Melons | Onions |
Peaches | Peppers |
Pears | Potatoes |
Plums | Tomatoes |
Another important component of the Mediterranean diet is whole grains. Whole grains are a good source of fiber, vitamins, and minerals. They can also help to lower your risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes.
- Brown rice
- Quinoa
- Oats
- Whole-wheat bread
- Whole-wheat pasta
Legumes are another important part of the Mediterranean diet. Legumes are a good source of protein, fiber, and iron. They can also help to lower your risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes.
- Beans
- Chickpeas
- Lentils
- Peas
Nuts and seeds are also a good addition to the Mediterranean diet. Nuts and seeds are a good source of protein, fiber, and healthy fats. They can also help to lower your risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes.
- Almonds
- Cashews
- Hazelnuts
- Pecans
- Pistachios
- Walnuts
Olive oil is the traditional fat used in the Mediterranean diet. Olive oil is a good source of healthy fats, which can help to lower your risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes.
The Mediterranean diet is a healthy and delicious way to eat. It is based on the foods that people living in the Mediterranean region have eaten for centuries, and it has been linked to a number of health benefits. If you are looking for a healthy way to eat, the Mediterranean diet is a great option.
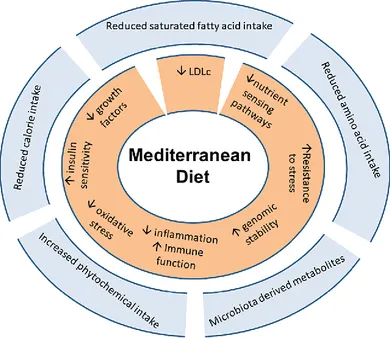
Mediterranean Diet and Disease Prevention
V. Benefits and Considerations for Adopting the Mediterranean Diet
Benefits of Adopting the Mediterranean Diet
Research shows that switching to the Mediterranean diet can bring various health benefits.
- Reduces the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- May reduce your risk for certain cancers like certain cancers such as breast cancer, colon cancer, and prostate cancer.
- May help with weight loss.
- Boosts cognitive function.
- Reduces the symptoms of metabolic syndrome.
- Improves sleep quality.
Considerations for Adopting the Mediterranean Diet
While the Mediterranean diet is generally considered safe, it may not be suitable for everyone. People with certain health conditions should be cautious about adopting this diet without first consulting with a healthcare professional.
Health Condition | Considerations |
|---|---|
Kidney disease | The Mediterranean diet can lead to increased levels of potassium in the blood, which can be dangerous for people with kidney disease. |
Iron deficiency | The Mediterranean diet is rich in plant-based foods, which can be low in iron. Iron deficiency can cause anemia, a condition that can lead to fatigue and other health problems. |
Vitamin B12 deficiency | The Mediterranean diet is not a good source of vitamin B12. Vitamin B12 is important for the health of the nervous system, and a deficiency can lead to a number of health problems, including anemia and fatigue. |

Benefits and Considerations for Adopting the Mediterranean Diet
VI. Conclusion
The Mediterranean diet is a testament to the power of tradition and the enduring connection between food and well-being. By embracing its principles, we honor our bodies and minds, nurturing them with the wholesome bounty that nature provides. May this culinary journey inspire you to make mindful choices, savor the flavors of life, and reap the countless health benefits that the Mediterranean diet offers. Remember, adopting this way of eating is not merely a change in diet but an investment in a healthier, more fulfilling future.